3
Data Transformation
Tidy Data Science with the Tidyverse and Tidymodels
W. Jake Thompson
https://tidyds-2021.wjakethompson.com · https://bit.ly/tidyds-2021
Tidy Data Science with the Tidyverse and Tidymodels is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
(Applied) Data Science
Example Data: babynames
library(babynames)babynames#> # A tibble: 1,924,665 x 5#> year sex name n prop#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>#> 1 1880 F Mary 7065 0.0724#> 2 1880 F Anna 2604 0.0267#> 3 1880 F Emma 2003 0.0205#> 4 1880 F Elizabeth 1939 0.0199#> 5 1880 F Minnie 1746 0.0179#> 6 1880 F Margaret 1578 0.0162#> 7 1880 F Ida 1472 0.0151#> 8 1880 F Alice 1414 0.0145#> 9 1880 F Bertha 1320 0.0135#> 10 1880 F Sarah 1288 0.0132#> # … with 1,924,655 more rowsYear, Sex assigned at birth, Name, Number, and Proportion (n / sum(n |year,gender))
Your turn 1
- Open the R Notebook materials/exercises/03-transform.Rmd
- Let's look at the
babynamesdata set - Run this code to view a summary of the data
skim(babynames)02:00
skim(babynames)#> ── Data Summary ────────────────────────#> Values #> Name babynames#> Number of rows 1924665 #> Number of columns 5 #> _______________________ #> Column type frequency: #> character 2 #> numeric 3 #> ________________________ #> Group variables None #> #> ── Variable type: character ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────#> skim_variable n_missing complete_rate min max empty n_unique whitespace#> 1 sex 0 1 1 1 0 2 0#> 2 name 0 1 2 15 0 97310 0#> #> ── Variable type: numeric ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────#> skim_variable n_missing complete_rate mean sd p0 p25 p50 p75 p100 hist #> 1 year 0 1 1975. 34.0 1880 1951 1985 2003 2017 ▁▂▃▅▇#> 2 n 0 1 181. 1533. 5 7 12 32 99686 ▇▁▁▁▁#> 3 prop 0 1 0.000136 0.00115 0.00000226 0.00000387 0.0000073 0.0000229 0.0815 ▇▁▁▁▁Isolating Data
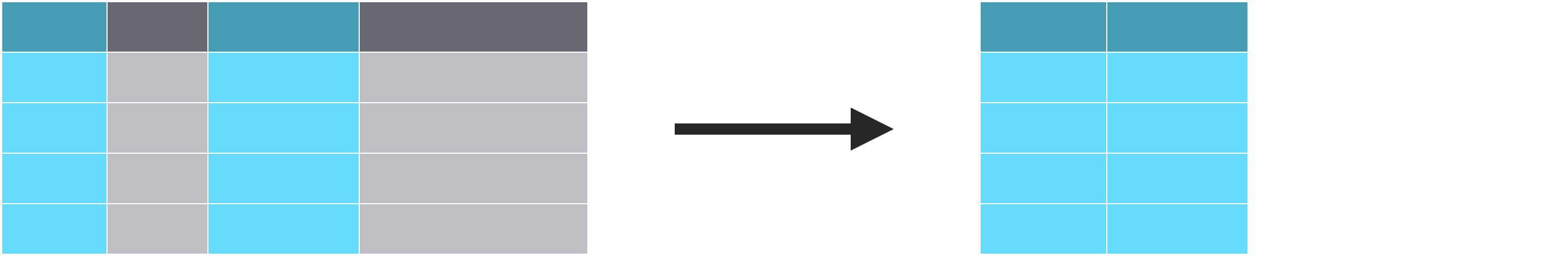
Extract variables with select()
Isolating Data

Extract variables with select()
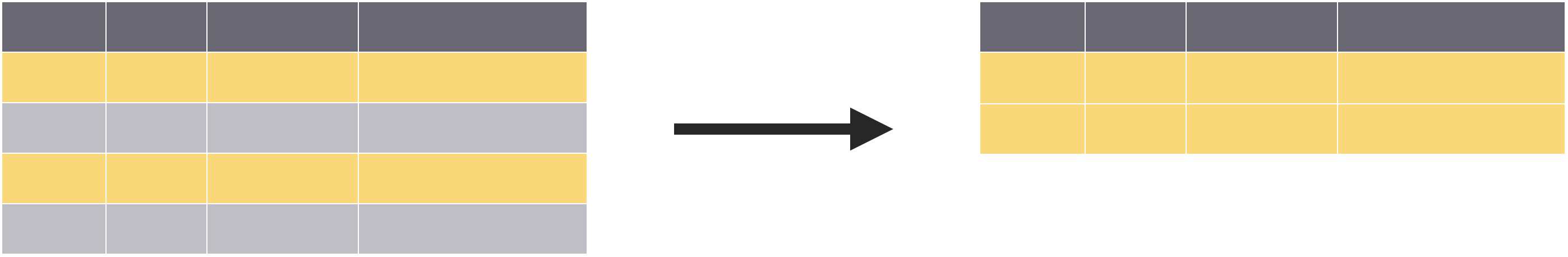
Extract cases with filter()
Isolating Data


Extract variables with select()
Extract cases with filter()
Arrange cases with arrange()
select()
select(.data, ...)
select(.data, ...)
Data to transform
select(.data, ...)
Name of column(s) to select, or select helper function
select(babynames, name, prop)| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Mary | 7065 | 0.072 |
| 1880 | F | Anna | 2604 | 0.027 |
| 1880 | F | Emma | 2003 | 0.021 |
| 1880 | F | Elizabeth | 1939 | 0.020 |
| 1880 | F | Minnie | 1746 | 0.018 |
| 1880 | F | Margaret | 1578 | 0.016 |
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | F | Alice | 1414 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Bertha | 1320 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Sarah | 1288 | 0.013 |
select(babynames, name, prop)| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Mary | 7065 | 0.072 |
| 1880 | F | Anna | 2604 | 0.027 |
| 1880 | F | Emma | 2003 | 0.021 |
| 1880 | F | Elizabeth | 1939 | 0.020 |
| 1880 | F | Minnie | 1746 | 0.018 |
| 1880 | F | Margaret | 1578 | 0.016 |
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | F | Alice | 1414 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Bertha | 1320 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Sarah | 1288 | 0.013 |
| name | prop |
|---|---|
| Mary | 0.072 |
| Anna | 0.027 |
| Emma | 0.021 |
| Elizabeth | 0.020 |
| Minnie | 0.018 |
| Margaret | 0.016 |
| Ida | 0.015 |
| Alice | 0.014 |
| Bertha | 0.014 |
| Sarah | 0.013 |
Your turn 2
- Alter the code to select just the
ncolumn
select(babynames, name, prop)02:00
Example Data: storms
storms#> # A tibble: 10,010 x 13#> name year month day hour lat long status category wind pressure#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <ord> <int> <int>#> 1 Amy 1975 6 27 0 27.5 -79 tropical d… -1 25 1013#> 2 Amy 1975 6 27 6 28.5 -79 tropical d… -1 25 1013#> 3 Amy 1975 6 27 12 29.5 -79 tropical d… -1 25 1013#> 4 Amy 1975 6 27 18 30.5 -79 tropical d… -1 25 1013#> 5 Amy 1975 6 28 0 31.5 -78.8 tropical d… -1 25 1012#> 6 Amy 1975 6 28 6 32.4 -78.7 tropical d… -1 25 1012#> 7 Amy 1975 6 28 12 33.3 -78 tropical d… -1 25 1011#> 8 Amy 1975 6 28 18 34 -77 tropical d… -1 30 1006#> 9 Amy 1975 6 29 0 34.4 -75.8 tropical s… 0 35 1004#> 10 Amy 1975 6 29 6 34 -74.8 tropical s… 0 40 1002#> # … with 10,000 more rows, and 2 more variables: ts_diameter <dbl>,#> # hu_diameter <dbl>Hurricane data; year, month, day, hour of report; position (lat/long); classification; category; wind speed; air pressure; diameter of the area with tropical storm winds; diameter of area with hurricane winds
select() helpers
: selects a range of columns
select(storms, name:pressure)- selects every column but
select(storms, -c(name, pressure))starts_with()/ends_with() selects based on start/end
select(storms, starts_with("w"))select(storms, ends_with("e"))select() helpers
contains() selects based on anywhere
select(storms, contains("d"))matches() selects based on expressions
select(storms, matches("^.{4}$"))any_of()/all_of() selects a set
select(storms, any_of(c("name", "names", "Name")))regex: name starts, has any character 4 times, then ends
Consider
Which of these is NOT a way to select the name and n columns together?
select(babynames, -c(year, sex, prop))select(babynames, name:n)select(babynames, starts_with("n"))select(babynames, ends_with("n"))01:00
select(babynames, -c(year, sex, prop))#> # A tibble: 1,924,665 x 2#> name n#> <chr> <int>#> 1 Mary 7065#> 2 Anna 2604#> 3 Emma 2003#> 4 Elizabeth 1939#> 5 Minnie 1746#> 6 Margaret 1578#> 7 Ida 1472#> 8 Alice 1414#> 9 Bertha 1320#> 10 Sarah 1288#> # … with 1,924,655 more rowsselect(babynames, name:n)#> # A tibble: 1,924,665 x 2#> name n#> <chr> <int>#> 1 Mary 7065#> 2 Anna 2604#> 3 Emma 2003#> 4 Elizabeth 1939#> 5 Minnie 1746#> 6 Margaret 1578#> 7 Ida 1472#> 8 Alice 1414#> 9 Bertha 1320#> 10 Sarah 1288#> # … with 1,924,655 more rowsselect(babynames, starts_with("n"))#> # A tibble: 1,924,665 x 2#> name n#> <chr> <int>#> 1 Mary 7065#> 2 Anna 2604#> 3 Emma 2003#> 4 Elizabeth 1939#> 5 Minnie 1746#> 6 Margaret 1578#> 7 Ida 1472#> 8 Alice 1414#> 9 Bertha 1320#> 10 Sarah 1288#> # … with 1,924,655 more rowsselect(babynames, ends_with("n"))#> # A tibble: 1,924,665 x 1#> n#> <int>#> 1 7065#> 2 2604#> 3 2003#> 4 1939#> 5 1746#> 6 1578#> 7 1472#> 8 1414#> 9 1320#> 10 1288#> # … with 1,924,655 more rowsfilter()
filter(.data, ...)
filter(.data, ...)
Data to transform
filter(.data, ...)
One or more logical tests. Filter returns each row where the test is TRUE
filter(babynames, name == "Ida")| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Mary | 7065 | 0.072 |
| 1880 | F | Anna | 2604 | 0.027 |
| 1880 | F | Emma | 2003 | 0.021 |
| 1880 | F | Elizabeth | 1939 | 0.020 |
| 1880 | F | Minnie | 1746 | 0.018 |
| 1880 | F | Margaret | 1578 | 0.016 |
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | F | Alice | 1414 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Bertha | 1320 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Sarah | 1288 | 0.013 |
filter(babynames, name == "Ida")| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Mary | 7065 | 0.072 |
| 1880 | F | Anna | 2604 | 0.027 |
| 1880 | F | Emma | 2003 | 0.021 |
| 1880 | F | Elizabeth | 1939 | 0.020 |
| 1880 | F | Minnie | 1746 | 0.018 |
| 1880 | F | Margaret | 1578 | 0.016 |
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | F | Alice | 1414 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Bertha | 1320 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Sarah | 1288 | 0.013 |
| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | M | Ida | 8 | 0.000 |
| 1881 | F | Ida | 1439 | 0.015 |
| 1881 | M | Ida | 5 | 0.000 |
| 1882 | F | Ida | 1673 | 0.014 |
| 1882 | M | Ida | 5 | 0.000 |
| 1883 | F | Ida | 1634 | 0.014 |
| 1883 | M | Ida | 5 | 0.000 |
| 1884 | F | Ida | 1882 | 0.014 |
| 1884 | M | Ida | 8 | 0.000 |
filter(babynames, name == "Ida")
Logical Tests
?Comparison
x
<
y
|
Less than |
x
>
y
|
Greater than |
x
==
y
|
Equal to |
x
<=
y
|
Less than or equal to |
x
>=
y
|
Greater than or equal to |
x
!=
y
|
Not equal to |
x
%in%
y
|
Group membership |
is.na(
x
)
|
Is missing (NA) |
!is.na(
x
)
|
Is not missing (not NA) |
Your turn 3
Use the logical operators to manipulate the babynames data to show:
- All of the names where
propis greater than .08 - All of the children named "Daenerys"
- All of the names that have a missing value for
n
(Hint: this should return an empty data set)
05:00
filter(babynames, prop > .08)#> # A tibble: 3 x 5#> year sex name n prop#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>#> 1 1880 M John 9655 0.0815#> 2 1880 M William 9532 0.0805#> 3 1881 M John 8769 0.0810filter(babynames, name == "Daenerys")#> # A tibble: 6 x 5#> year sex name n prop#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>#> 1 2012 F Daenerys 21 0.0000108#> 2 2013 F Daenerys 68 0.0000354#> 3 2014 F Daenerys 86 0.0000441#> 4 2015 F Daenerys 82 0.0000422#> 5 2016 F Daenerys 101 0.0000524#> 6 2017 F Daenerys 110 0.0000587filter(babynames, is.na(n))#> # A tibble: 0 x 5#> # … with 5 variables: year <dbl>, sex <chr>, name <chr>, n <int>, prop <dbl>filter(babynames, name == "Ida", year == 1880)| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Mary | 7065 | 0.072 |
| 1880 | F | Anna | 2604 | 0.027 |
| 1880 | F | Emma | 2003 | 0.021 |
| 1880 | F | Elizabeth | 1939 | 0.020 |
| 1880 | F | Minnie | 1746 | 0.018 |
| 1880 | F | Margaret | 1578 | 0.016 |
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | F | Alice | 1414 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Bertha | 1320 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Sarah | 1288 | 0.013 |
filter(babynames, name == "Ida", year == 1880)| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Mary | 7065 | 0.072 |
| 1880 | F | Anna | 2604 | 0.027 |
| 1880 | F | Emma | 2003 | 0.021 |
| 1880 | F | Elizabeth | 1939 | 0.020 |
| 1880 | F | Minnie | 1746 | 0.018 |
| 1880 | F | Margaret | 1578 | 0.016 |
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | F | Alice | 1414 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Bertha | 1320 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Sarah | 1288 | 0.013 |
| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | M | Ida | 8 | 0.000 |
Specify multiple logical conditions that must be met. Listing comma separated values is equivalent to "AND"/&
Boolean operators
?base::Logic
a
&
b
|
and |
a
|
b
|
or |
xor(
a, b
)
|
Exactly or |
!
a
|
not |
a
%in%
c(a, b)
|
One of (in) |
xor -> one is true and one is false
Your turn 4
Use the Boolean operators to manipulate the babynames data to show:
- Girls named Sea
- Names that were used by exactly 5 or 6 children in 1880
- Names that are one of Acura, Lexus, or Yugo
05:00
filter(babynames, name == "Sea", sex == "F")#> # A tibble: 2 x 5#> year sex name n prop#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>#> 1 1982 F Sea 5 0.00000276#> 2 1998 F Sea 5 0.00000258filter(babynames, name == "Sea" & sex == "F")#> # A tibble: 2 x 5#> year sex name n prop#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>#> 1 1982 F Sea 5 0.00000276#> 2 1998 F Sea 5 0.00000258filter(babynames, n %in% c(5, 6), year == 1880)#> # A tibble: 455 x 5#> year sex name n prop#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>#> 1 1880 F Abby 6 0.0000615#> 2 1880 F Aileen 6 0.0000615#> 3 1880 F Alba 6 0.0000615#> 4 1880 F Alda 6 0.0000615#> 5 1880 F Alla 6 0.0000615#> 6 1880 F Alverta 6 0.0000615#> 7 1880 F Ara 6 0.0000615#> 8 1880 F Ardelia 6 0.0000615#> 9 1880 F Ardella 6 0.0000615#> 10 1880 F Arrie 6 0.0000615#> # … with 445 more rowsfilter(babynames, (n == 5 | n == 6) & year == 1880)#> # A tibble: 455 x 5#> year sex name n prop#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>#> 1 1880 F Abby 6 0.0000615#> 2 1880 F Aileen 6 0.0000615#> 3 1880 F Alba 6 0.0000615#> 4 1880 F Alda 6 0.0000615#> 5 1880 F Alla 6 0.0000615#> 6 1880 F Alverta 6 0.0000615#> 7 1880 F Ara 6 0.0000615#> 8 1880 F Ardelia 6 0.0000615#> 9 1880 F Ardella 6 0.0000615#> 10 1880 F Arrie 6 0.0000615#> # … with 445 more rowsfilter(babynames, name %in% c("Acura", "Lexus", "Yugo"))#> # A tibble: 57 x 5#> year sex name n prop#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>#> 1 1990 F Lexus 36 0.0000175 #> 2 1990 M Lexus 12 0.00000558#> 3 1991 F Lexus 102 0.0000502 #> 4 1991 M Lexus 16 0.00000755#> 5 1992 F Lexus 193 0.0000963 #> 6 1992 M Lexus 25 0.0000119 #> 7 1993 F Lexus 285 0.000145 #> 8 1993 M Lexus 30 0.0000145 #> 9 1994 F Lexus 381 0.000195 #> 10 1994 F Acura 6 0.00000308#> # … with 47 more rowsfilter(babynames, name == "Acura" | name == "Lexus" | name == "Yugo")#> # A tibble: 57 x 5#> year sex name n prop#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>#> 1 1990 F Lexus 36 0.0000175 #> 2 1990 M Lexus 12 0.00000558#> 3 1991 F Lexus 102 0.0000502 #> 4 1991 M Lexus 16 0.00000755#> 5 1992 F Lexus 193 0.0000963 #> 6 1992 M Lexus 25 0.0000119 #> 7 1993 F Lexus 285 0.000145 #> 8 1993 M Lexus 30 0.0000145 #> 9 1994 F Lexus 381 0.000195 #> 10 1994 F Acura 6 0.00000308#> # … with 47 more rowsCommon mistakes:
- collapsing multiple tests into one (i.e.,
10 < n < 20instead of10 < n, n < 20) - Stringing together many tests when you could use %in%
arrange()
arrange(.data, ...)
arrange(.data, ...)
Data to transform
arrange(.data, ...)
One or more columns to order by. Additional columns are used to break ties.
arrange(babynames, n)| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1965 | M | Russell | 5,649 | 0.003 |
| 1935 | M | Jimmy | 4,173 | 0.004 |
| 1891 | M | William | 6,763 | 0.062 |
| 2000 | M | Kevin | 12,667 | 0.006 |
| 1956 | M | Johnny | 6,640 | 0.003 |
| 1918 | F | Gladys | 8,735 | 0.007 |
| 1971 | M | Stephen | 13,105 | 0.007 |
| 1898 | M | James | 5,321 | 0.040 |
| 1994 | F | Kaitlyn | 6,686 | 0.003 |
| 1933 | F | Margaret | 15,239 | 0.015 |
arrange(babynames, n)| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1965 | M | Russell | 5,649 | 0.003 |
| 1935 | M | Jimmy | 4,173 | 0.004 |
| 1891 | M | William | 6,763 | 0.062 |
| 2000 | M | Kevin | 12,667 | 0.006 |
| 1956 | M | Johnny | 6,640 | 0.003 |
| 1918 | F | Gladys | 8,735 | 0.007 |
| 1971 | M | Stephen | 13,105 | 0.007 |
| 1898 | M | James | 5,321 | 0.040 |
| 1994 | F | Kaitlyn | 6,686 | 0.003 |
| 1933 | F | Margaret | 15,239 | 0.015 |
| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1935 | M | Jimmy | 4,173 | 0.004 |
| 1898 | M | James | 5,321 | 0.040 |
| 1965 | M | Russell | 5,649 | 0.003 |
| 1956 | M | Johnny | 6,640 | 0.003 |
| 1994 | F | Kaitlyn | 6,686 | 0.003 |
| 1891 | M | William | 6,763 | 0.062 |
| 1918 | F | Gladys | 8,735 | 0.007 |
| 2000 | M | Kevin | 12,667 | 0.006 |
| 1971 | M | Stephen | 13,105 | 0.007 |
| 1933 | F | Margaret | 15,239 | 0.015 |
Your turn 5
- Arrange
babynamesbyn. Addpropas a second (tiebreaking) variable to arrange by. - What is the smallest value of
n?
02:00
arrange(babynames, n, prop)# A tibble: 1,924,665 x 5 year sex name n prop <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> 1 2007 M Aaban 5 0.00000226 2 2007 M Aareon 5 0.00000226 3 2007 M Aaris 5 0.00000226 4 2007 M Abd 5 0.00000226 5 2007 M Abdulazeez 5 0.00000226 6 2007 M Abdulhadi 5 0.00000226 7 2007 M Abdulhamid 5 0.00000226 8 2007 M Abdulkadir 5 0.00000226 9 2007 M Abdulraheem 5 0.0000022610 2007 M Abdulrahim 5 0.00000226# … with 1,924,655 more rowsDescending Order
arrange(babynames, desc(n))
| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1965 | M | Russell | 5,649 | 0.003 |
| 1935 | M | Jimmy | 4,173 | 0.004 |
| 1891 | M | William | 6,763 | 0.062 |
| 2000 | M | Kevin | 12,667 | 0.006 |
| 1956 | M | Johnny | 6,640 | 0.003 |
| 1918 | F | Gladys | 8,735 | 0.007 |
| 1971 | M | Stephen | 13,105 | 0.007 |
| 1898 | M | James | 5,321 | 0.040 |
| 1994 | F | Kaitlyn | 6,686 | 0.003 |
| 1933 | F | Margaret | 15,239 | 0.015 |
Descending Order
arrange(babynames, desc(n))
| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1965 | M | Russell | 5,649 | 0.003 |
| 1935 | M | Jimmy | 4,173 | 0.004 |
| 1891 | M | William | 6,763 | 0.062 |
| 2000 | M | Kevin | 12,667 | 0.006 |
| 1956 | M | Johnny | 6,640 | 0.003 |
| 1918 | F | Gladys | 8,735 | 0.007 |
| 1971 | M | Stephen | 13,105 | 0.007 |
| 1898 | M | James | 5,321 | 0.040 |
| 1994 | F | Kaitlyn | 6,686 | 0.003 |
| 1933 | F | Margaret | 15,239 | 0.015 |
| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1933 | F | Margaret | 15,239 | 0.015 |
| 1971 | M | Stephen | 13,105 | 0.007 |
| 2000 | M | Kevin | 12,667 | 0.006 |
| 1918 | F | Gladys | 8,735 | 0.007 |
| 1891 | M | William | 6,763 | 0.062 |
| 1994 | F | Kaitlyn | 6,686 | 0.003 |
| 1956 | M | Johnny | 6,640 | 0.003 |
| 1965 | M | Russell | 5,649 | 0.003 |
| 1898 | M | James | 5,321 | 0.040 |
| 1935 | M | Jimmy | 4,173 | 0.004 |
Your turn 6
- Use
desc()to find the names with the highestprop. - Which names have the largest values of
n?
02:00
arrange(babynames, desc(prop))# A tibble: 1,924,665 x 5 year sex name n prop <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> 1 1880 M John 9655 0.0815 2 1881 M John 8769 0.0810 3 1880 M William 9532 0.0805 4 1883 M John 8894 0.0791 5 1881 M William 8524 0.0787 6 1882 M John 9557 0.0783 7 1884 M John 9388 0.0765 8 1882 M William 9298 0.0762 9 1886 M John 9026 0.075810 1885 M John 8756 0.0755# … with 1,924,655 more rowsarrange(babynames, desc(n))# A tibble: 1,924,665 x 5 year sex name n prop <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> 1 1947 F Linda 99686 0.0548 2 1948 F Linda 96209 0.0552 3 1947 M James 94756 0.0510 4 1957 M Michael 92695 0.0424 5 1947 M Robert 91642 0.0493 6 1949 F Linda 91016 0.0518 7 1956 M Michael 90620 0.0423 8 1958 M Michael 90520 0.0420 9 1948 M James 88588 0.049710 1954 M Michael 88514 0.0428# … with 1,924,655 more rows%>%
Consider
How would you do the following to the babynames data:
- Filter to only the names Sansa and Arya;
- Arrange by
nameand thenyear; and - Remove the
propvariable
# A tibble: 67 x 4 year sex name n <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> 1 1982 M Arya 12 2 1983 M Arya 7 3 1984 M Arya 9 4 1985 M Arya 20 5 1986 F Arya 5 6 1986 M Arya 18 7 1987 M Arya 22 8 1988 F Arya 5 9 1988 M Arya 2210 1989 M Arya 30# … with 57 more rows02:00
Nesting
babynames
Nesting
babynames
filter(babynames, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya"))
Nesting
babynames
filter(babynames, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya"))
arrange(filter(babynames, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya")), name, year)
Nesting
babynames
filter(babynames, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya"))
arrange(filter(babynames, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya")), name, year)
select(arrange(filter(babynames, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya")), name, year), -prop)
Nesting
babynames
filter(babynames, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya"))
arrange(filter(babynames, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya")), name, year)
select(arrange(filter(babynames, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya")), name, year), -prop)
select(arrange(filter(babynames, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya")), name, year), -prop)
Start with babynames
Then filter to Sansa and Arya
Then arrange by name and year
Finally remove prop
Intermediate objects
bn1 <- babynames
Intermediate objects
bn1 <- babynames
bn2 <- filter(bn1, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya"))
Intermediate objects
bn1 <- babynames
bn2 <- filter(bn1, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya"))
bn3 <- arrange(bn2, name, year)
Intermediate objects
bn1 <- babynames
bn2 <- filter(bn1, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya"))
bn3 <- arrange(bn2, name, year)
bn4 <- select(bn3, -prop)
Intermediate objects
bn1 <- babynames
bn2 <- filter(bn1, name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya"))
bn3 <- arrange(bn2, name, year)
bn4 <- select(bn3, -prop)
What are all these objects in my environment window??
Your code should tell the story of what you are doing to the data
Let's tell a story
I:
- Tumble out of bed
Let's tell a story
I:
Tumble out of bed
Stumble to the kitchen
Let's tell a story
I:
Tumble out of bed
Stumble to the kitchen
Pour myself a cup of ambition
Let's tell a story
I:
Tumble out of bed
Stumble to the kitchen
Pour myself a cup of ambition
Yawn
Let's tell a story
I:
Tumble out of bed
Stumble to the kitchen
Pour myself a cup of ambition
Yawn
Stretch
Let's tell a story
I:
Tumble out of bed
Stumble to the kitchen
Pour myself a cup of ambition
Yawn
Stretch
Try to come to live
What story does this tell?
try(come_to_live( stretch(yawn(pour(stumble(tumble(I, out_of = "bed"), to = "the kitchen"), who = "myself", unit = "cup", what = "ambition")))))Turn the story into code
ITurn the story into code
tumble(I, out_of = "bed")Turn the story into code
stumble(tumble(I, out_of = "bed"), to = "the kitchen")Turn the story into code
pour(stumble(tumble(I, out_of = "bed"), to = "the kitchen"), who = "myself", unit = "cup", what = "ambition")Turn the story into code
yawn(pour(stumble(tumble(I, out_of = "bed"), to = "the kitchen"), who = "myself", unit = "cup", what = "ambition"))Turn the story into code
stretch(yawn(pour(stumble(tumble(I, out_of = "bed"), to = "the kitchen"), who = "myself", unit = "cup", what = "ambition")))Turn the story into code
try(come_to_live( stretch(yawn(pour(stumble(tumble(I, out_of = "bed"), to = "the kitchen"), who = "myself", unit = "cup", what = "ambition")))))We understand because we wrote it, but can others? Remember before we built this up.
%>%
%>%
Pass the output of one function to the first argument of the next
me1 <- "I"
me2 <- tumble(me1, out_of = "bed")
me3 <- stumble(me2, to = "the kitchen")
me1 <- "I"
me2 <- tumble(me1, out_of = "bed")
me3 <- stumble(me2, to = "the kitchen")
me1 <- "I"
me2 <- tumble(me1, out_of = "bed")
me3 <- stumble(me2, to = "the kitchen")
me1 <- "I"
me2 <- tumble(me1, out_of = "bed")
me3 <- stumble(me2, to = "the kitchen")
me1 <- "I"
me2 <- tumble(me1, out_of = "bed")
me3 <- stumble(me2, to = "the kitchen")
I %>%
tumble(out_of = "bed") %>%
stumble(to = "the kitchen")
Tell a story
I %>% tumble(out_of = "bed") %>% stumble(to = "the kitchen") %>% pour(who = "myself", unit = "cup", what = "ambition") %>% yawn() %>% stretch() %>% try(come_to_live())Piping in the tidyverse
Functions take a data frame as their first argument, and return a data frame.
select(.data, ...)
filter(.data, ...)
arrange(.data, ...)
Reconsider
How would you do the following to the babynames data:
- Filter to only the names Sansa and Arya;
- Arrange by
nameand thenyear; and - Remove the
propvariable
# A tibble: 67 x 4 year sex name n <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> 1 1982 M Arya 12 2 1983 M Arya 7 3 1984 M Arya 9 4 1985 M Arya 20 5 1986 F Arya 5 6 1986 M Arya 18 7 1987 M Arya 22 8 1988 F Arya 5 9 1988 M Arya 2210 1989 M Arya 30# … with 57 more rowsbabynames %>% filter(name %in% c("Sansa", "Arya")) %>% arrange(name, year) %>% select(-prop)#> # A tibble: 67 x 4#> year sex name n#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int>#> 1 1982 M Arya 12#> 2 1983 M Arya 7#> 3 1984 M Arya 9#> 4 1985 M Arya 20#> 5 1986 F Arya 5#> 6 1986 M Arya 18#> 7 1987 M Arya 22#> 8 1988 F Arya 5#> 9 1988 M Arya 22#> 10 1989 M Arya 30#> # … with 57 more rowsYour turn 7
Use %>% to write a sequence of functions that:
- Filter
babynamesto just the females that were born in 2015. - Select the
nameandncolumns. - Arrange the results so that the most popular names are at the top.
04:00
babynames %>% filter(sex == "F", year == 2015) %>% select(name, n) %>% arrange(desc(n))# A tibble: 19,074 x 2 name n <chr> <int> 1 Emma 20435 2 Olivia 19669 3 Sophia 17402 4 Ava 16361 5 Isabella 15594 6 Mia 14892 7 Abigail 12390 8 Emily 11780 9 Charlotte 1139010 Harper 10291# … with 19,064 more rowsYour turn 8
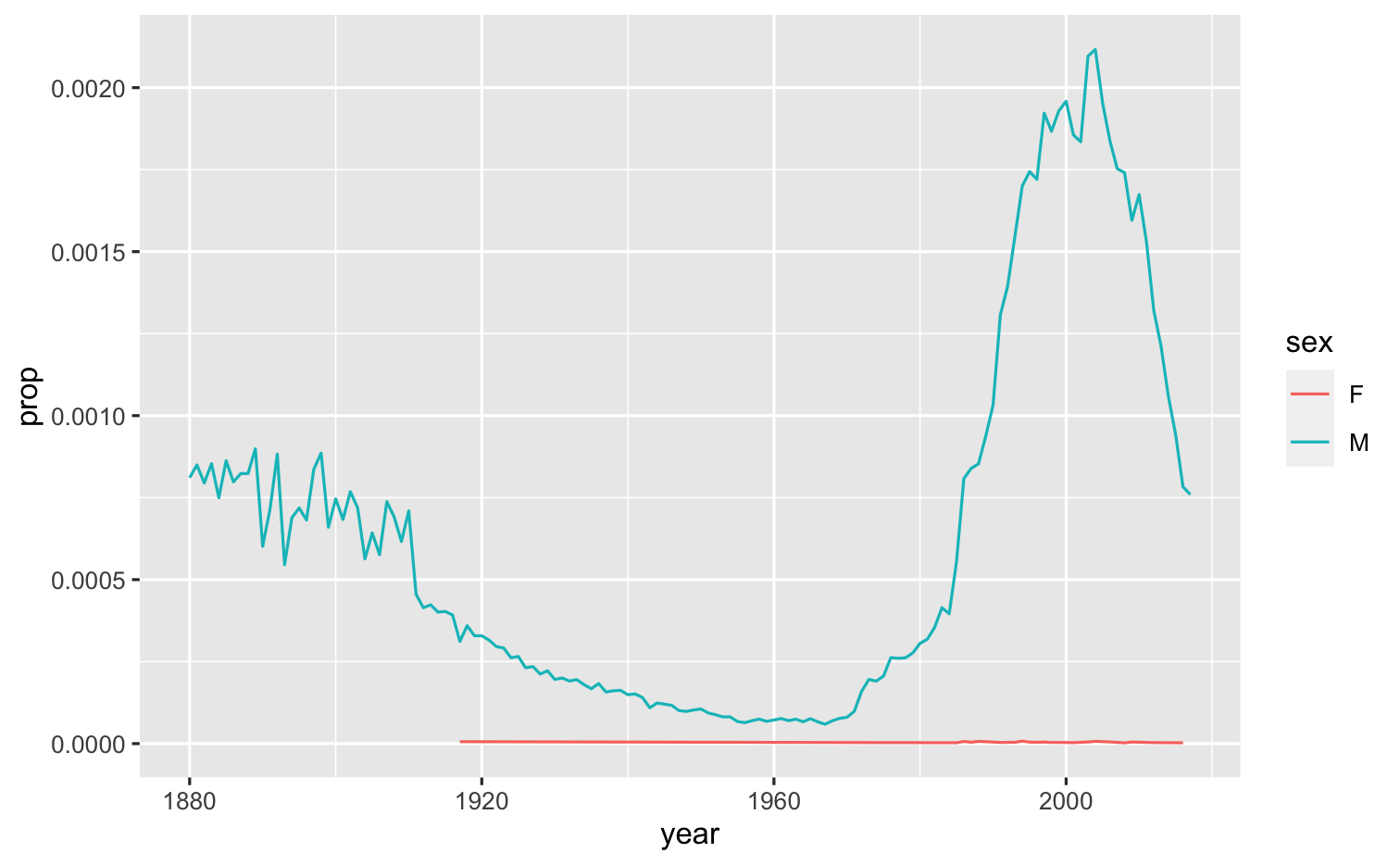
Combine your new data skills to make a plot showing the popularity of your name over time.
- Trim
babynamesto just the rows that contain yourname. - Trim the result to just the columns that are needed for your plot.
- Plot the results as a line graph with
yearon the x-axis andpropon the y-axis, coloredsex.
04:00
What names are the most popular?
What is popularity?
We can assess popularity through:
What is popularity?
We can assess popularity through:
- Sums - a large number of children have the name when we sum across years.
What is popularity?
We can assess popularity through:
Sums - a large number of children have the name when we sum across years.
Ranks - the name consistently ranks among the top names from year to year.
Consider
Do we have enough information to:
- Calculate the total number of children with each name?
- Rank the names within each year?
Deriving information
Compile data with summarize()
Deriving information

Compile data with summarize()
Analyze groups with group_by()
Deriving information


Compile data with summarize()
Analyze groups with group_by()
Make new variables with mutate()
summarize()
summarize(.data, ...)
summarize(.data, ...)
Data to summarize
summarize(.data, ...)
Summaries to calculate
summarize(babynames, total = sum(n), max = max(n))| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Mary | 7065 | 0.072 |
| 1880 | F | Anna | 2604 | 0.027 |
| 1880 | F | Emma | 2003 | 0.021 |
| 1880 | F | Elizabeth | 1939 | 0.020 |
| 1880 | F | Minnie | 1746 | 0.018 |
| 1880 | F | Margaret | 1578 | 0.016 |
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | F | Alice | 1414 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Bertha | 1320 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Sarah | 1288 | 0.013 |
summarize(babynames, total = sum(n), max = max(n))| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Mary | 7065 | 0.072 |
| 1880 | F | Anna | 2604 | 0.027 |
| 1880 | F | Emma | 2003 | 0.021 |
| 1880 | F | Elizabeth | 1939 | 0.020 |
| 1880 | F | Minnie | 1746 | 0.018 |
| 1880 | F | Margaret | 1578 | 0.016 |
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | F | Alice | 1414 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Bertha | 1320 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Sarah | 1288 | 0.013 |
| total | max |
|---|---|
| 348120517 | 99686 |
Your turn 9
Use summarize() to compute three statistics about the data:
- The first (minimum) year in the data set
- The last (maximum) year in the data set
- The total number of unique names in the data.
Hint: Use the functions min(), max(), and n_distinct().
03:00
Your turn 10
Extract the rows for children named Khaleesi.
- How many children have been named Khaleesi?
- What was the first year Khaleesi appeared in the data?
04:00
group_by()
group_by(.data, ...)
group_by(.data, ...)
Data to group
group_by(.data, ...)
Variables to group by
group_by(babynames, sex)#> # A tibble: 1,924,665 x 5#> # Groups: sex [2]#> year sex name n prop#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>#> 1 1880 F Mary 7065 0.0724#> 2 1880 F Anna 2604 0.0267#> 3 1880 F Emma 2003 0.0205#> 4 1880 F Elizabeth 1939 0.0199#> 5 1880 F Minnie 1746 0.0179#> 6 1880 F Margaret 1578 0.0162#> 7 1880 F Ida 1472 0.0151#> 8 1880 F Alice 1414 0.0145#> 9 1880 F Bertha 1320 0.0135#> 10 1880 F Sarah 1288 0.0132#> # … with 1,924,655 more rowsWhat has changed? Additional meta data being printed.
Grouped summaries
babynames %>% group_by(sex) %>% summarize(num_names = n_distinct(name))#> # A tibble: 2 x 2#> sex num_names#> <chr> <int>#> 1 F 67046#> 2 M 40927Your turn 11
Calculate popularity by determining the total number of children given each name.
- Use
group_by()andsummarize()to calculate the total number of children that have been given each name, by sex. Arrange the results to show the most popular names first.
Bonus:
Create a bar plot of the 10 most popular names, with
nameon the x-axis and total children on the y-axis.
05:00
babynames %>% group_by(name, sex) %>% summarize(total = sum(n)) %>% arrange(desc(total))# A tibble: 107,973 x 3# Groups: name [97,310] name sex total <chr> <chr> <int> 1 James M 5150472 2 John M 5115466 3 Robert M 4814815 4 Michael M 4350824 5 Mary F 4123200 6 William M 4102604 7 David M 3611329 8 Joseph M 2603445 9 Richard M 256308210 Charles M 2386048# … with 107,963 more rowsbabynames %>% group_by(name, sex) %>% summarize(total = sum(n), .groups = "drop") %>% arrange(desc(total)) %>% slice_max(total, n = 10) %>% ggplot(mapping = aes(x = fct_reorder(name, desc(total)), y = total)) + geom_col(mapping = aes(fill = sex)) + scale_fill_brewer() + labs(x = "Name", y = "Total Children") + theme_bw()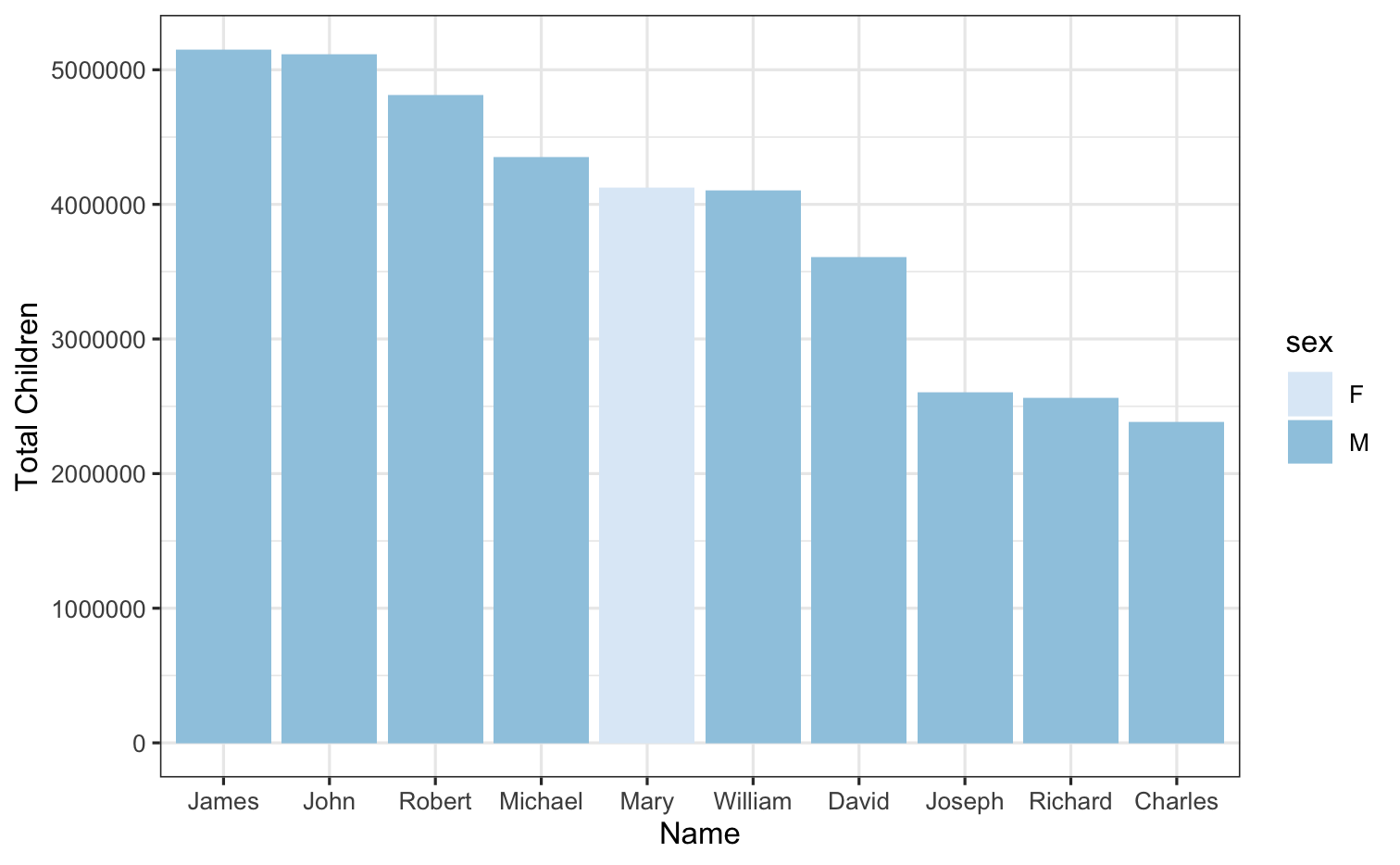
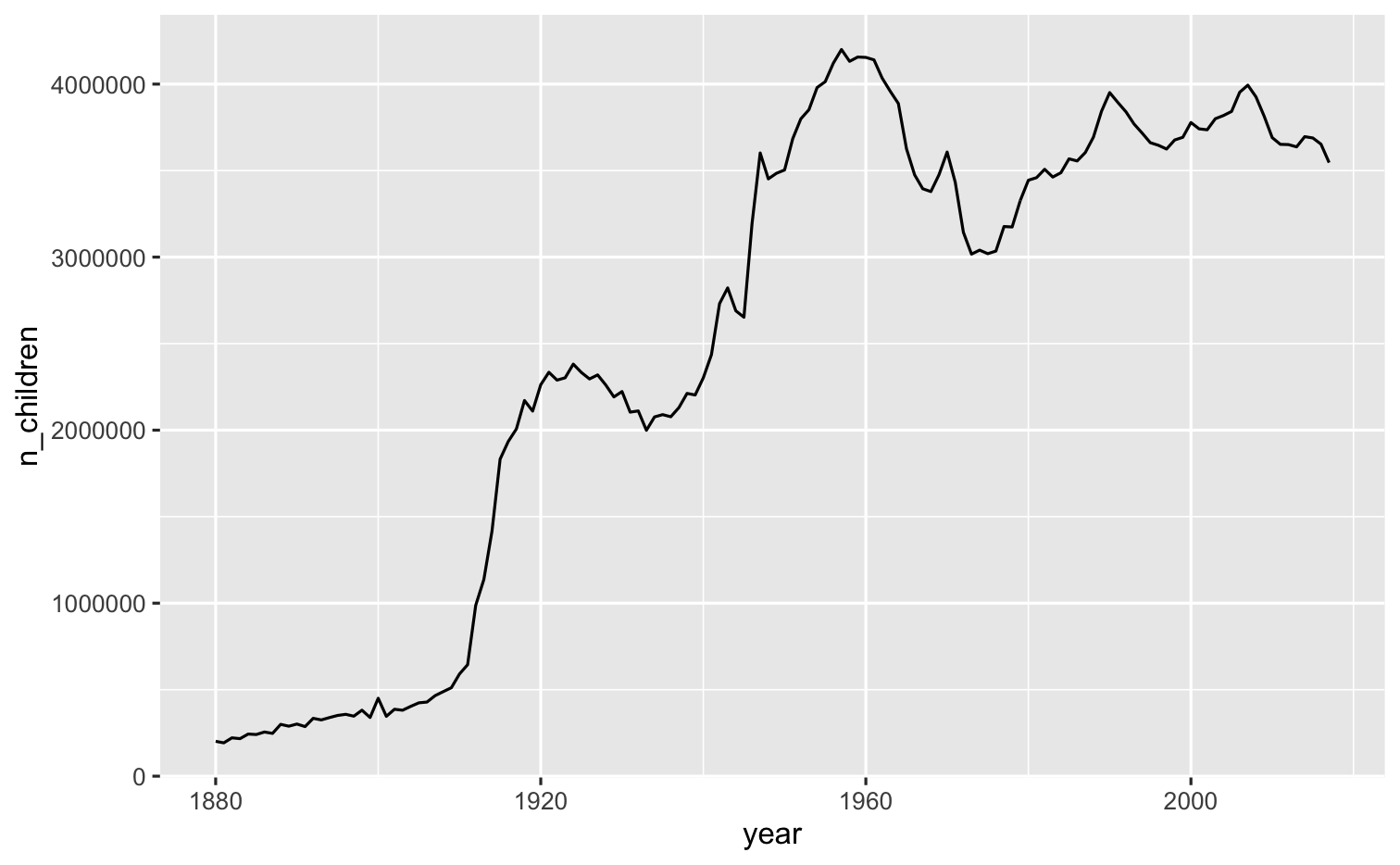
Your turn 12
Use grouping to calculate the number of children born each year.
Plot the results as a line graph.
05:00
What does this affect our measure of popularity?
mutate()
mutate(.data, ...)
mutate(.data, ...)
Data to mutate
mutate(.data, ...)
Additional variables to calculate
mutate(babynames, percent = round(prop * 100, digits = 2))| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Mary | 7065 | 0.072 |
| 1880 | F | Anna | 2604 | 0.027 |
| 1880 | F | Emma | 2003 | 0.021 |
| 1880 | F | Elizabeth | 1939 | 0.020 |
| 1880 | F | Minnie | 1746 | 0.018 |
| 1880 | F | Margaret | 1578 | 0.016 |
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | F | Alice | 1414 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Bertha | 1320 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Sarah | 1288 | 0.013 |
mutate(babynames, percent = round(prop * 100, digits = 2))| year | sex | name | n | prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Mary | 7065 | 0.072 |
| 1880 | F | Anna | 2604 | 0.027 |
| 1880 | F | Emma | 2003 | 0.021 |
| 1880 | F | Elizabeth | 1939 | 0.020 |
| 1880 | F | Minnie | 1746 | 0.018 |
| 1880 | F | Margaret | 1578 | 0.016 |
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 |
| 1880 | F | Alice | 1414 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Bertha | 1320 | 0.014 |
| 1880 | F | Sarah | 1288 | 0.013 |
| year | sex | name | n | prop | percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | F | Mary | 7065 | 0.072 | 7.24 |
| 1880 | F | Anna | 2604 | 0.027 | 2.67 |
| 1880 | F | Emma | 2003 | 0.021 | 2.05 |
| 1880 | F | Elizabeth | 1939 | 0.020 | 1.99 |
| 1880 | F | Minnie | 1746 | 0.018 | 1.79 |
| 1880 | F | Margaret | 1578 | 0.016 | 1.62 |
| 1880 | F | Ida | 1472 | 0.015 | 1.51 |
| 1880 | F | Alice | 1414 | 0.014 | 1.45 |
| 1880 | F | Bertha | 1320 | 0.014 | 1.35 |
| 1880 | F | Sarah | 1288 | 0.013 | 1.32 |
min_rank()
Lowest value get the lowest rank, i.e., 1.
min_rank(c(50, 40, 60, 75, 50))#> [1] 2 1 4 5 2min_rank()
Lowest value get the lowest rank, i.e., 1.
min_rank(c(50, 40, 60, 75, 50))#> [1] 2 1 4 5 2To give highest values the rank of 1, use desc()
min_rank(desc(c(50, 40, 60, 75, 50)))#> [1] 3 5 2 1 3Your turn 13
Use mutate() and min_rank() to rank each row in babynames from largest prop to lowest prop.
The highest prop should have a rank of 1.
03:00
babynames %>% mutate(rank = min_rank(desc(prop)))# A tibble: 1,924,665 x 6 year sex name n prop rank <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <int> 1 1880 F Mary 7065 0.0724 14 2 1880 F Anna 2604 0.0267 709 3 1880 F Emma 2003 0.0205 1131 4 1880 F Elizabeth 1939 0.0199 1192 5 1880 F Minnie 1746 0.0179 1427 6 1880 F Margaret 1578 0.0162 1683 7 1880 F Ida 1472 0.0151 1897 8 1880 F Alice 1414 0.0145 2039 9 1880 F Bertha 1320 0.0135 227910 1880 F Sarah 1288 0.0132 2387# … with 1,924,655 more rowsYour turn 14
What is each name's median rank?
- Compute each
name's rank with eachyearandsex. - Compute the median rank across years for each
name, within eachsex. - Sort the results from highest median rank to lowest.
05:00
babynames %>% group_by(year, sex) %>% mutate(rank = min_rank(desc(prop))) %>% group_by(name, sex) %>% summarize(score = median(rank)) %>% arrange(score)# A tibble: 107,973 x 3# Groups: name [97,310] name sex score <chr> <chr> <dbl> 1 Mary F 1 2 James M 3 3 John M 3 4 William M 4 5 Robert M 6 6 Michael M 7.5 7 Charles M 9 8 Elizabeth F 10 9 Joseph M 10 10 Thomas M 11 # … with 107,963 more rowsRecap: Single table verbs





Extract variables with select()
Extract cases with filter()
Arrange cases with arrange()
Compile data with summarize()
Make new variables with mutate()
Example Data: nycflights13
library(nycflights13)flights#> # A tibble: 336,776 x 19#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time sched_arr_time#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> <int>#> 1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830 819#> 2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850 830#> 3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923 850#> 4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004 1022#> 5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812 837#> 6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740 728#> 7 2013 1 1 555 600 -5 913 854#> 8 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 709 723#> 9 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 838 846#> 10 2013 1 1 558 600 -2 753 745#> # … with 336,766 more rows, and 11 more variables: arr_delay <dbl>,#> # carrier <chr>, flight <int>, tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>,#> # air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>Which airlines had the longest delays?
distinct(flights, carrier)#> # A tibble: 16 x 1#> carrier#> <chr> #> 1 UA #> 2 AA #> 3 B6 #> 4 DL #> 5 EV #> 6 MQ #> 7 US #> 8 WN #> 9 VX #> 10 FL #> 11 AS #> 12 9E #> 13 F9 #> 14 HA #> 15 YV #> 16 OOairlines#> # A tibble: 16 x 2#> carrier name #> <chr> <chr> #> 1 9E Endeavor Air Inc. #> 2 AA American Airlines Inc. #> 3 AS Alaska Airlines Inc. #> 4 B6 JetBlue Airways #> 5 DL Delta Air Lines Inc. #> 6 EV ExpressJet Airlines Inc. #> 7 F9 Frontier Airlines Inc. #> 8 FL AirTran Airways Corporation#> 9 HA Hawaiian Airlines Inc. #> 10 MQ Envoy Air #> 11 OO SkyWest Airlines Inc. #> 12 UA United Air Lines Inc. #> 13 US US Airways Inc. #> 14 VX Virgin America #> 15 WN Southwest Airlines Co. #> 16 YV Mesa Airlines Inc.Mutating joins use information from one data set to add variables to another data set (like mutate())
Mutating joins use information from one data set to add variables to another data set (like mutate())
Filtering joins use information from one data set to extract cases from another data set (like filter())
Toy data for practice
left_join()
left_join(heros, homes, by = "hero")right_join()
right_join(heros, homes, by = "hero")full_join()
full_join(heros, homes, by = "hero")inner_join()
inner_join(heros, homes, by = "hero")Your turn 15
Which airlines had the largest arrival delays (arr_delay)? Complete the code below.
flights %>%
drop_na(arr_delay) %>%
%>% # 1. Join airlines to flights
group_by( ) %>%
%>% # 2. Compute the average arrival delay
arrange(desc(delay))
06:00
flights %>% drop_na(arr_delay) %>% left_join(airlines, by = "carrier") %>% group_by(name) %>% summarize(delay = mean(arr_delay)) %>% arrange(desc(delay))#> # A tibble: 16 x 2#> name delay#> <chr> <dbl>#> 1 Frontier Airlines Inc. 21.9 #> 2 AirTran Airways Corporation 20.1 #> 3 ExpressJet Airlines Inc. 15.8 #> 4 Mesa Airlines Inc. 15.6 #> 5 SkyWest Airlines Inc. 11.9 #> 6 Envoy Air 10.8 #> 7 Southwest Airlines Co. 9.65 #> 8 JetBlue Airways 9.46 #> 9 Endeavor Air Inc. 7.38 #> 10 United Air Lines Inc. 3.56 #> 11 US Airways Inc. 2.13 #> 12 Virgin America 1.76 #> 13 Delta Air Lines Inc. 1.64 #> 14 American Airlines Inc. 0.364#> 15 Hawaiian Airlines Inc. -6.92 #> 16 Alaska Airlines Inc. -9.93Non-matching names
Use a named vector to match on variables with different names.
heroes %>% left_join(enemies, by = c("hero" = "avenger"))Mutating joins use information from one data set to add variables to another data set (like mutate())
Filtering joins use information from one data set to extract cases from another data set (like filter())
semi_join()
semi_join(heros, homes, by = "hero")anti_join()
anti_join(heros, homes, by = "hero")Your turn 16
How many airports in the airports data were serviced by flights originating in New York?
Notice that the column to join on is named faa in the airports data set and dest in the flights data set.
05:00
airports %>% semi_join(flights, by = c("faa" = "dest")) %>% distinct()#> # A tibble: 101 x 8#> faa name lat lon alt tz dst tzone #> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <chr> #> 1 ABQ Albuquerque International… 35.0 -107. 5355 -7 A America/Denv…#> 2 ACK Nantucket Mem 41.3 -70.1 48 -5 A America/New_…#> 3 ALB Albany Intl 42.7 -73.8 285 -5 A America/New_…#> 4 ANC Ted Stevens Anchorage Intl 61.2 -150. 152 -9 A America/Anch…#> 5 ATL Hartsfield Jackson Atlant… 33.6 -84.4 1026 -5 A America/New_…#> 6 AUS Austin Bergstrom Intl 30.2 -97.7 542 -6 A America/Chic…#> 7 AVL Asheville Regional Airport 35.4 -82.5 2165 -5 A America/New_…#> 8 BDL Bradley Intl 41.9 -72.7 173 -5 A America/New_…#> 9 BGR Bangor Intl 44.8 -68.8 192 -5 A America/New_…#> 10 BHM Birmingham Intl 33.6 -86.8 644 -6 A America/Chic…#> # … with 91 more rowsData Transformation

Tidy Data Science with the Tidyverse and Tidymodels
W. Jake Thompson
https://tidyds-2021.wjakethompson.com · https://bit.ly/tidyds-2021
Tidy Data Science with the Tidyverse and Tidymodels is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.